Definition
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) is a cybersecurity solution designed to protect endpoints, such as computers, servers, mobile devices, and IoT devices, from various types of cyber threats.
Unlike traditional antivirus solutions that primarily focus on preventing known threats, an EDR solution goes beyond and aims to detect and respond to both known and unknown threats in real-time.
How EDR Works
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) solutions operate by continuously monitoring endpoint devices for any suspicious behavior and potential security threats. These EDR security solutions record and store endpoint-system-level behaviors, utilizing advanced data analytics techniques to detect anomalies, provide contextual information, block malicious activities, and suggest remediation steps to restore affected systems.
EDR solutions typically consist of three main components:
- Endpoint Monitoring: EDR monitor endpoint devices in real-time, collecting data on system activities, network connections, and user behavior. This continuous and comprehensive visibility into endpoint data allows for the early detection of potential threats.
- Threat Detection: Using advanced threat detection techniques such as machine learning and behavioral analysis, response endpoint detection solutions identify potential security threats. This proactive approach ensures that both known and unknown threats are detected promptly.
- Response and Remediation: EDR provide automated response and remediation capabilities, such as isolating affected devices, blocking malicious activity, and offering remediation suggestions. This helps security teams to quickly mitigate threats and restore normal operations.
Key features
- Focus on Endpoints: EDR is centered around monitoring and securing individual endpoints such as computers, servers, and mobile devices.
- Endpoint Visibility: Provides visibility into endpoint activities, processes, and behaviors to detect and respond to threats at the device level.
- Monitoring of Endpoints: It continuously monitors endpoints for suspicious activities and behaviors. This proactive approach enables rapid threat detection and response, minimizing the potential impact of attacks.
- Threat Hunting: It allows the security team to proactively search for signs of compromise within an organization’s endpoints. This hunting process can uncover dormant threats that have evaded initial detection.
- Memory and Process Monitoring: Monitors system memory and processes to detect and respond to threats that may be operating in memory without leaving traditional file traces.
- Forensic Investigation of Endpoints: It offers forensic insights into an attack’s origin, propagation, and impact. This information is invaluable for understanding attack vectors (specific paths that can be exploited to break into an IT system) and improving future defenses.
- Automation and Orchestration: Some EDR incorporate automation to streamline incident response. They can automatically execute predefined actions when certain criteria are met, reducing manual intervention and response time.
Benefits
- Threat Detection: Its approach ensures the identification of known threats, including zero-day exploits and fileless attacks.
- Reduced Dwell Time: By swiftly detecting and responding to threats, it can reduce the time attackers have to infiltrate and operate within an environment undetected.
- Some Visibility: It provides visibility into endpoint activities, aiding in threat detection and helping security teams make informed decisions.
- Improved Compliance: It often assists organizations in meeting regulatory requirements by maintaining a comprehensive record of endpoint activities and security measures.
- Actionable Intelligence: Provides actionable intelligence that enhances an organization’s ability to respond effectively to security incidents, ensuring prompt management and retrieval of relevant security information.
Threat Detection and Response
Threat detection and response is a critical component of EDR. These solutions employ various techniques to identify potential security threats, ensuring a robust defense against cyberattacks.
- Behavioral Analysis: Endpoint detection solutions analyze system behavior to identify potential security threats. By understanding normal behavior patterns, they can detect deviations that may indicate malicious activity.
- Machine Learning: EDR leverage machine learning algorithms to identify patterns and anomalies in system behavior. This allows for the detection of sophisticated threats that may not be caught by traditional methods.
- Signature-Based Detection: EDR security solutions use signature-based detection to identify known security threats. This method relies on predefined signatures of known malware and other malicious activities.
Once a potential security threat is detected, EDR solutions provide automated response and remediation capabilities, such as:
- Isolating Affected Devices: EDR can isolate affected devices to prevent the spread of malware, ensuring that the threat is contained.
- Blocking Malicious Activity: Endpoint detection solutions can block malicious activity, such as suspicious network connections, to protect the security environment.
- Providing Remediation Suggestions: EDR offer remediation suggestions to restore affected systems, helping security teams to quickly and effectively address the threat.
AI and Machine Learning in EDR
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) play a pivotal role in enhancing the capabilities of endpoint detection solutions. These technologies are used to analyze system behavior, identify patterns and anomalies, and detect potential security threats with greater accuracy.
EDR use AI and ML in various ways, including:
- Behavioural Analysis: AI and ML algorithms are employed to analyze system behavior and identify potential security threats. This allows for the detection of subtle and sophisticated attacks that may evade traditional detection methods.
- Anomaly Detection: AI and ML algorithms are used to identify anomalies in system behavior that may indicate a security threat. By recognizing deviations from normal behavior, these algorithms can detect previously unknown threats.
- Predictive Analytics: AI and ML algorithms are utilized to predict potential security threats based on historical data and system behaviour. This proactive approach helps in anticipating and mitigating threats before they can cause significant damage.
Scalability and Adaptability
EDR is designed to be scalable and adaptable, making it suitable for organizations of all sizes and security needs. It can be deployed on-premises, in the cloud, or in a hybrid environment, providing flexibility in implementation.
EDR is scalable in various ways, including:
- Endpoint Coverage: Endpoint detection solutions can cover thousands of endpoints, making them ideal for large organizations with extensive IT infrastructure.
- Data Analytics: EDR can analyze large volumes of data, ensuring that even complex security environments are effectively monitored and protected.
- Integration with Existing Security Tools: EDR can seamlessly integrate with existing security tools, enhancing the overall security stack and providing a more comprehensive defense against threats.
Endpoint detection solutions are also adaptable in various ways, including:
- Customizable Policies: EDR allow organizations to create customizable policies tailored to their specific security needs, ensuring that the solution aligns with their security strategy.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Endpoint detection solutions provide real-time monitoring, enabling organizations to respond quickly to potential security threats and minimize the impact of attacks.
- Continuous Updates: EDR offer continuous updates, ensuring that organizations stay protected against the latest security threats and evolving attack vectors.
By leveraging the scalability and adaptability of EDR, organizations can enhance their endpoint security posture and effectively protect against a wide range of cyber threats.
Challenges and what to consider
While EDR presents the above benefits, its implementation and utilization comes with certain challenges:
Resource Intensity
Due to continuous monitoring and analysis, it can consume significant system resources, potentially impacting endpoint performance.
Data Privacy
Collecting and analyzing endpoint data raises concerns about privacy and compliance. Your organization must ensure that data handling aligns with regulations and best practices.
Tuning and False Positives
It may generate false positive alerts if not properly tuned. To reduce unnecessary alerts and focus on genuine threats, the system must be fine-tuned
Skill Requirement
Effective implementation requires skilled cybersecurity personnel who understand the technology, threat landscape, and incident response procedures.
Integration with Existing Infrastructure
Integrating it seamlessly with your organization’s existing security infrastructure can be complex, requiring careful planning and coordination.
Evolution of Threats
Cyber threats are constantly evolving, and new tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) are developed by attackers. It relies on known patterns and behaviors, so they may not immediately detect novel or sophisticated threats.
Zero-Day Exploits
It may not be able to detect zero-day exploits, which are attacks exploiting vulnerabilities that are not yet known to the vendor or the security community. Since there are no predefined signatures for these exploits, they may go undetected until security vendors develop and deploy updates.
Resource Constraints
In some cases, organizations may not have the resources or expertise to fully configure and manage it effectively, limiting their ability to detect and respond to threats.
User Behavior Variability
EDR often use behavioral analytics to identify anomalies. However, legitimate variations in user behavior or system activity can sometimes trigger false positives or be challenging to distinguish from malicious behavior.
Human Factor
Social engineering attacks, which often involve manipulating individuals to divulge confidential information, may not be directly addressed. Human awareness and education are crucial components in defending against such attacks.

While EDR focuses on endpoint threats, but it may need NDR for broader network visibility and detecting threats that bypass endpoints.
EDR vs. traditional antivirus
While traditional antivirus solutions remain a vital part of cybersecurity, EDR offers a more comprehensive approach to threat detection and response:
- Near Real-Time Monitoring: Traditional antiviruses often perform periodic scans while the other continuously monitors for suspicious activities, offering real-time visibility into endpoint behavior.
- Better Incident Response: Traditional antivirus solutions primarily focus on isolating and removing threats without detailed investigation, whereas EDR facilitates automated and orchestrated incident response actions.
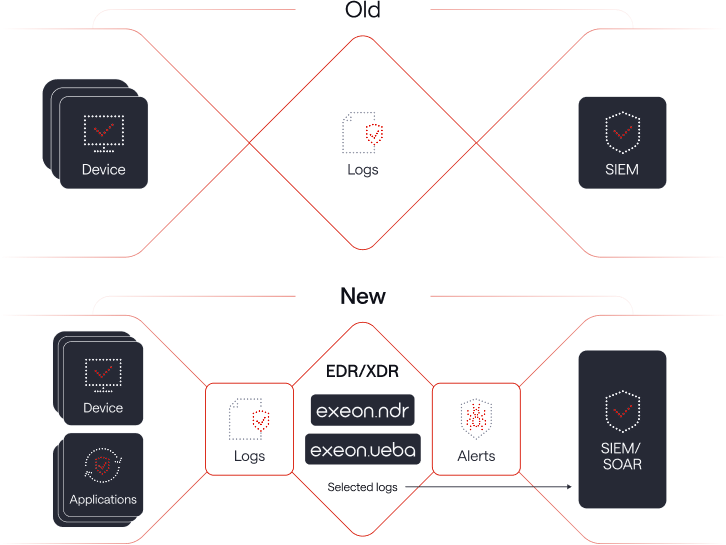
Why it’s not enough: NDR to the rescue
While EDR focuses on endpoint activities, it may not have full visibility into network-level threats.
Network Detection and Response (NDR) solutions complement it by monitoring and detecting threats at the network level.
This has been extremely critical in cases such as the recent worldwide Windows outage related to an EDR issue.
NDR and EDR/XDR: Evolution of cyber defense stacks
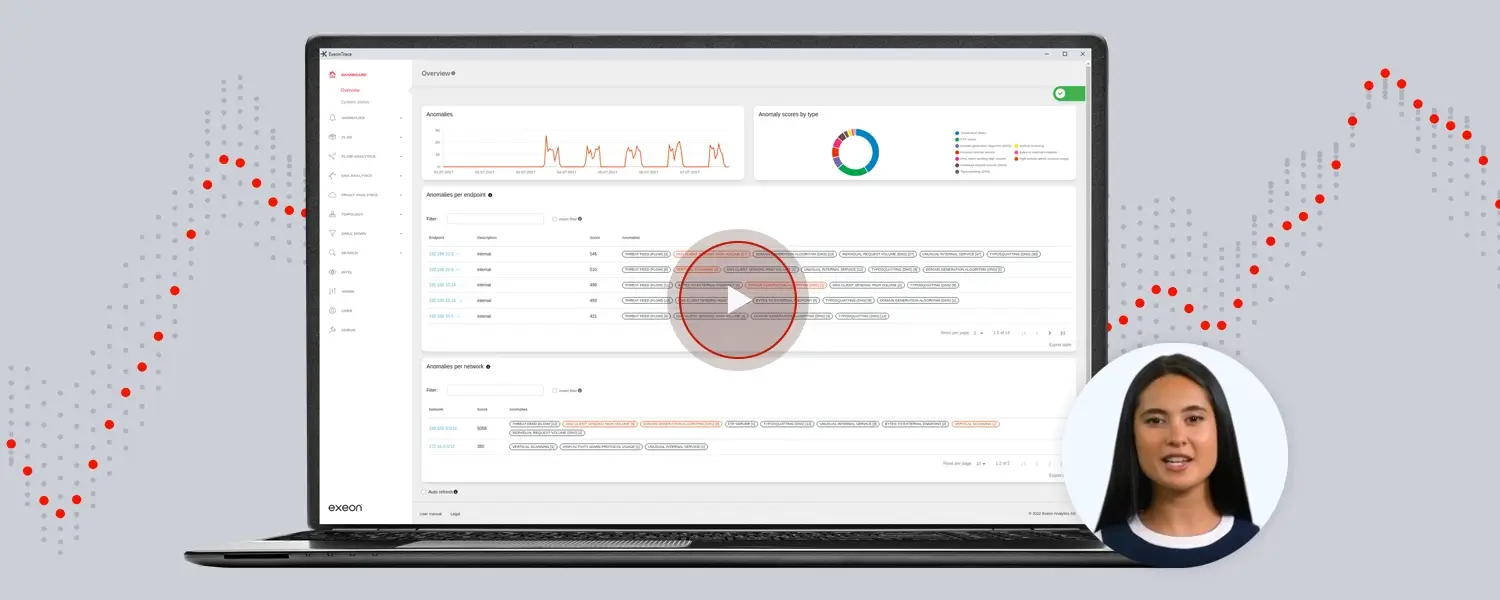
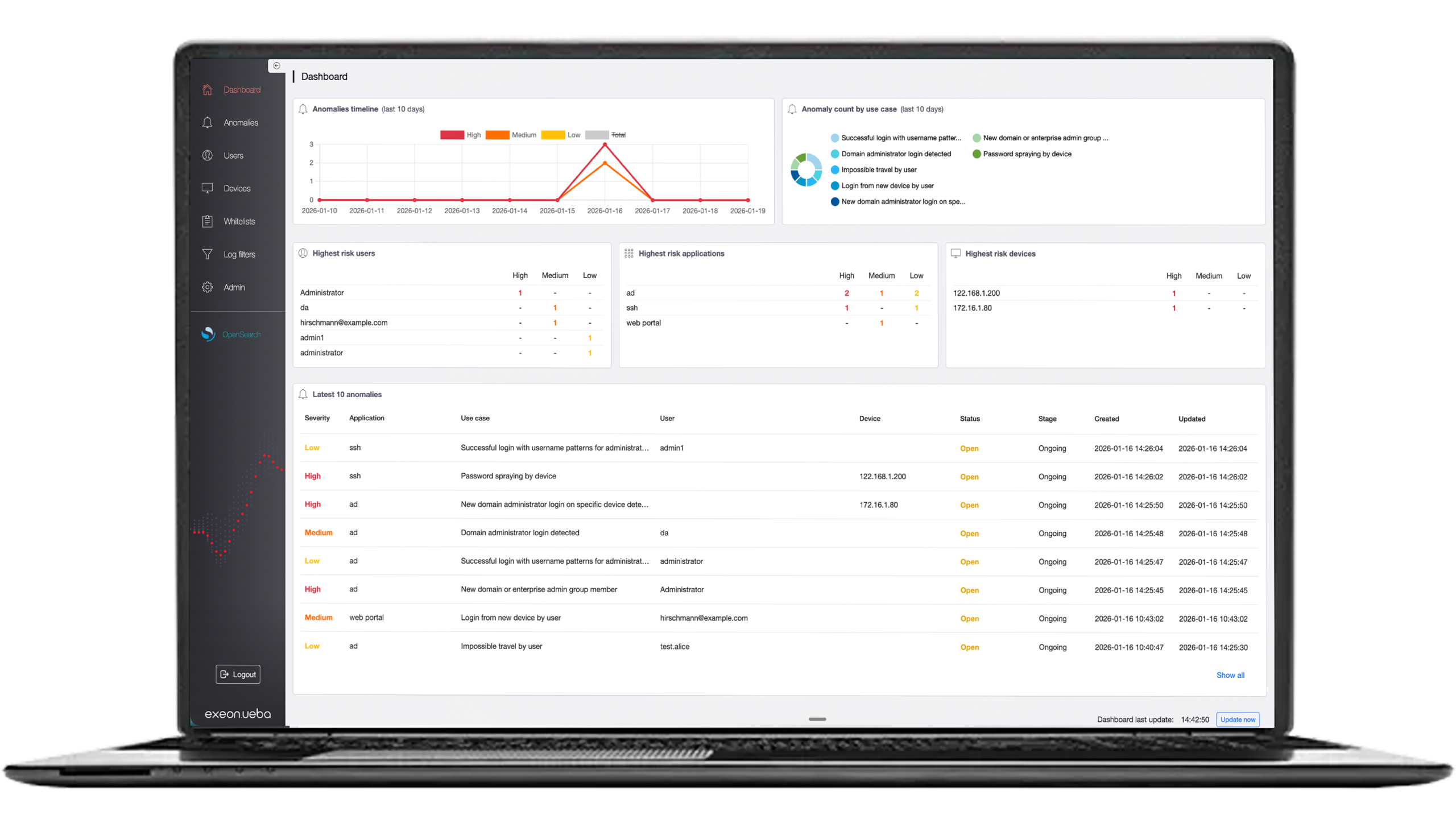
Exeon.NDR: amplifying security & effectiveness
Exeon.NDR, a Swiss-made NDR solution used by governmental institutions and large organizations, emerges as a transformative force in the realm of endpoint security, seamlessly integrating with EDR to bolster their capabilities.
By enriching EDR with comprehensive network data insights, Exeon.NDR enhances the efficacy of endpoint threat detection. This innovative approach equips security teams with unparalleled visibility into network data flows, enabling proactive responses to potential threats before they escalate.
Exeon.NDR’s collaboration with EDR creates a powerful synergy that amplifies the strengths of both solutions, solidifying your organization’s endpoint security posture and fostering a proactive stance against a wide range of cyber threats.