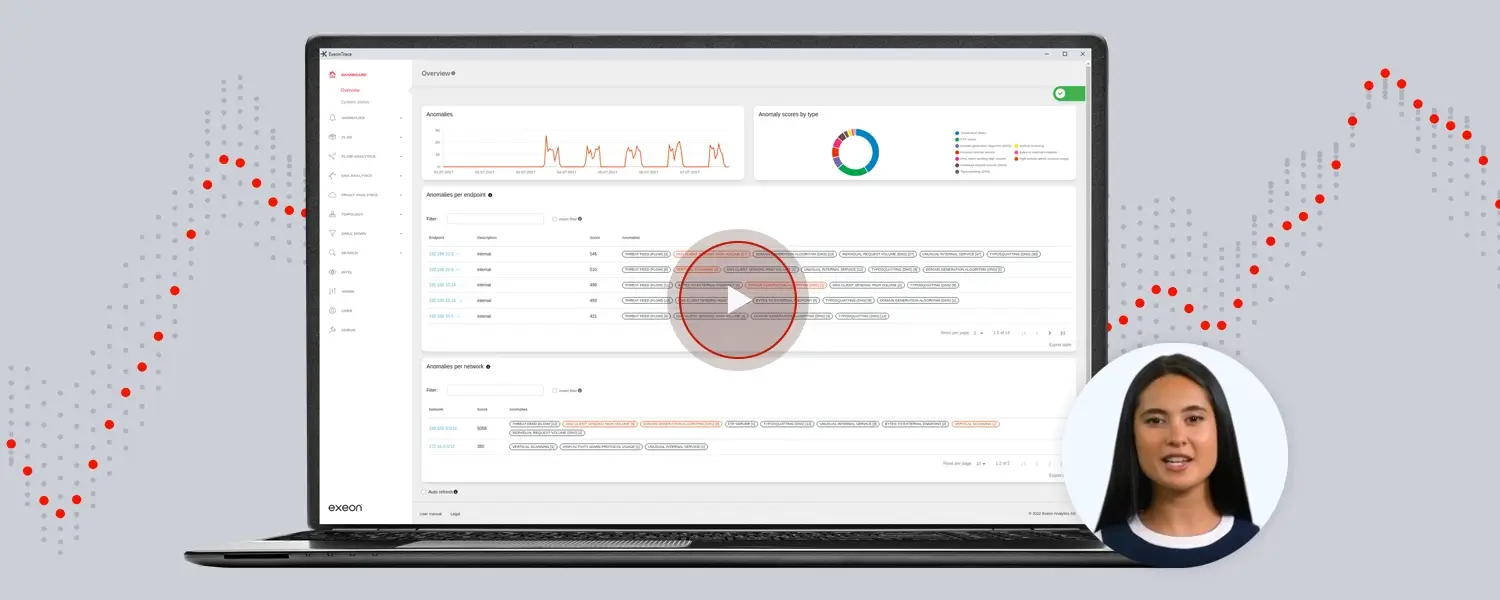
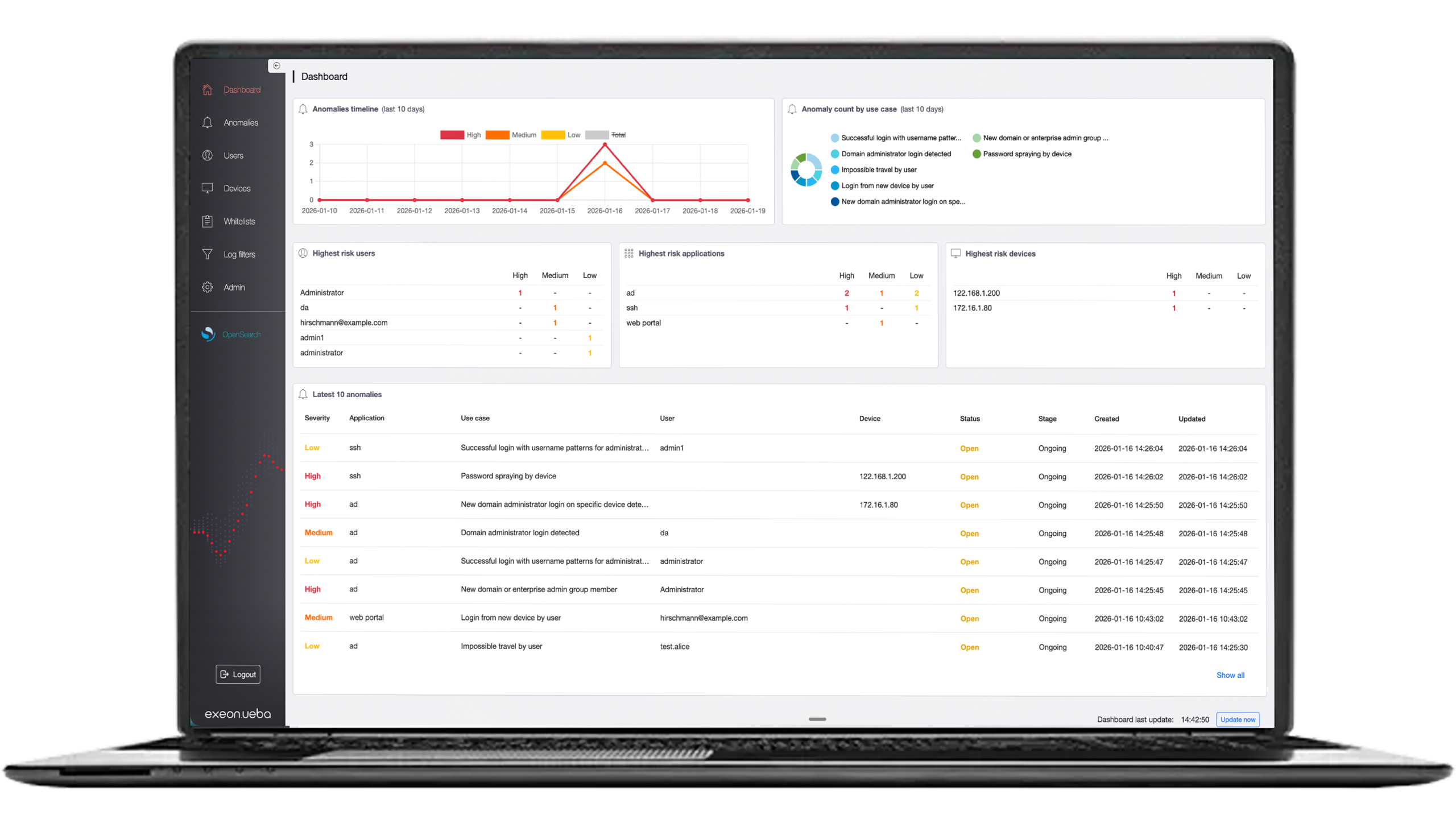
How Does SIEM Work?
SIEM combines two essential functions: Security Information Management (SIM) and Security Event Management (SEM), and is known as a mature cybersecurity solution. A SIEM system collects and analyzes log and event data from various sources to detect and respond to threats.
Components & functions
Data collection
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems collect data from a wide array of sources, including most network devices (such as firewalls or routers), servers, applications, security appliances (like antivirus software and intrusion detection/prevention systems), and even cloud-based services.
This data consists of logs, event records, and other security-related information. SIEM integrates with other security solutions to enhance the overall security operations of an organization.
Data Integration
SIEM integrates with a wide array of third-party applications and data sources, making it versatile in its application. For example, it can work in tandem with intrusion detection systems (IDS/IPS), antivirus software, and vulnerability scanners.
Data Analysis and Correlation
SIEM systems excel at analyzing and correlating security data from a multitude of sources to pinpoint potential security risk factors. This process begins with the aggregation of log data from various systems, such as firewalls, servers, and applications.
Once collected, the data is normalized into a standardized format, making it easier to analyze. Advanced SIEM systems leverage machine learning and artificial intelligence to enhance threat detection accuracy and minimize false positives.
By applying sophisticated rules and algorithms, SIEM systems can detect patterns and anomalies that may indicate security threats, providing a robust layer of protection against cyberattacks.
Normalization and correlation
After collecting data, SIEM systems normalize and correlate it. The security team uses this normalized data to identify and respond to security threats.
Normalization involves translating data from various formats and sources into a standardized format for analysis. Correlation entails examining the data for patterns, relationships, and anomalies that might indicate a security threat.
- Search and Analysis: Users are able to perform searches, queries, and data analysis to uncover patterns, trends, and anomalies within the collected data.
- Visualizations: Some SIEMs offer extra data visualization tools to create charts, graphs, and dashboards to help users understand their data at a glance.
- Scalability This technology can scale to handle large volumes of data and can be deployed on-premises or in the cloud.
- Customization: Users can create custom apps and add-ons to extend the functionality and to meet specific business needs.
Security Information Management
SIM is a cornerstone of SIEM systems. It involves the meticulous collection, storage, and analysis of security-related data from diverse sources, including firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and antivirus software.
SIM provides security analysts with a centralized view across the organization, enabling them to identify potential security threats and vulnerabilities more effectively.
By consolidating SIM, organizations can streamline their security operations and enhance their overall security posture.
Real-Time Monitoring
Real-time monitoring is a pivotal feature of SIEM systems, empowering security analysts to keep a vigilant eye on security events as they unfold.
This capability allows for the swift identification and response to potential security threats, significantly reducing the mean time to detect (MTTD) and mean time to respond (MTTR) to security incidents.
With real-time monitoring, security teams can stay ahead of emerging threats, ensuring a proactive approach to cybersecurity.
Incident Response
SIEM solutions play an indispensable role in incident response, equipping security teams with the necessary tools and information to address security incidents promptly.
These SIEM systems provide alerts, notifications, and incident response workflows that streamline the response process. By automating many aspects of incident response, SIEM systems reduce the time and effort required to manage security incidents, allowing security teams to focus on more strategic tasks.
This automation not only enhances the efficiency of incident response but also ensures a more coordinated and effective approach to mitigating security threats.
Data storage and retention
Security event data are stored for an extended period, often in a secure and tamper-evident manner. This historical data can be valuable for compliance purposes or forensic investigations.
- Reporting and Dashboards: These SIEM systems offer customizable reporting capabilities and dashboards. Security teams can create reports to provide insights into the organization’s security posture, trying to track trends, identify vulnerabilities, and demonstrate compliance with security policies to stakeholders.
- Compliance: SIEM solutions can help in meeting regulatory compliance requirements. As they provide a centralized platform, making it easier to demonstrate compliance with various industry standards and regulations.
Benefits
Improved threat detection
- Improvements through the continuous monitoring of various data sources, including network traffic, system logs, and application activity.
- By correlating information from multiple sources, it becomes possible to identify complex attack patterns that might go unnoticed by individual security tools.
- Real-time alerting and threat detection capabilities should enable organizations to respond quicker to security incidents.
Compliance management
- Regulatory compliance is a significant concern for many organizations, particularly those in industries such as finance, healthcare, and government. SIEM solutions simplify compliance management by generating detailed logs and reports that align with regulatory requirements and industry standards.
- SIEM systems provide a centralized platform for collecting and storing the data necessary for compliance reporting. This includes audit logs, access control records, and user activity logs. Security teams can easily generate compliance reports, which are often required for regulatory audits and assessments.
- Compliance is not only about meeting legal requirements but also about demonstrating a commitment to robust security practices. This technology can help organizations showcase their diligence in safeguarding sensitive data and adhering to security best practices.
Historical analysis
- SIEM’s data retention capabilities enable historical analysis of security events and incidents. This historical data can be invaluable for several purposes, including forensic investigations, trend analysis, and understanding the evolution of attack techniques.
- Forensic Analysis: When a security incident occurs, access to historical data allows security teams to trace the attack back to its source and understand the full scope of the breach. This information is crucial for evidence collection and legal proceedings.
Integration
- One of the strengths of SIEM solutions is their ability to integrate with other security tools and technologies. This integration enhances an organization’s overall security posture by streamlining security operations and increasing overall effectiveness.
- SIEMs can integrate with antivirus software, intrusion detection (IDS) or prevention systems (IPS), vulnerability scanners, identity and access management (IAM) solutions, and more. This interoperability aims for a coordinated and orchestrated response to security incidents.

SIEMs are greatly enhanced by NDR with real-time network visibility and detecting threats that traditional logs might miss—read more further below.
Challenges
While a Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) solution contributes to an organization’s cybersecurity defenses, it’s important to recognize that, like all technological solutions, these systems introduce their distinct set of considerations and complexities.
Implementing a SIEM system effectively requires adherence to best practices to ensure robust security management. As a result, SIEM solutions constitute just one element within the larger framework of a comprehensive security strategy.
Complex Implementation
Setting up a SIEM solution is complex and time-consuming. It often involves integrating with various systems, configuring rules, and fine-tuning to ensure it effectively monitors and analyzes security events.
Data Overload
As such SIEM systems generate a vast amount of data and alerts. It’s challenging to distinguish between routine events and potential threats, which may result in alert fatigue, where security teams may start to ignore alerts or miss important signals.
Tuning and False Positives
These systems may produce false positives, leading to unnecessary investigations and wasted time. Tuning the SIEM solution to reduce false positives while not missing actual threats requires ongoing effort and expertise.
Skill and Expertise
Effective use of these solutions requires trained personnel who understand both cybersecurity and the specific SIEM platform. Hiring or training staff with the necessary skills can be a challenge.
Integration
Ensuring that the SIEM solution can integrate with a wide range of existing systems and technologies can be complex. New systems and applications may need custom connectors or configurations.
Scalability
As an organization grows, its data and infrastructure also expand. These solutions should scale accordingly to handle increased data volumes and monitoring needs.
Cost
Implementing a SIEM solution can be expensive, not just in terms of software and hardware costs but also personnel for configuration, management, and ongoing maintenance. Additionally, the cost can increase with the need for additional features and functionality.
Regulatory Compliance
Organizations in regulated industries often require compliance with specific data protection and reporting requirements. Configuring security operation solutions such as SIEMs to meet these standards can be challenging.
Incident Response
A security system can detect potential security incidents, but the challenge lies in responding effectively. Organizations need well-defined incident response procedures and personnel trained to execute them.
Data Privacy and Legal Issues
Collecting and storing vast amounts of security data can raise concerns about data privacy and legal issues. Organizations must ensure that they comply with data protection laws and regulations.
Data Retention and Storage
The volume of data generated and stored by such systems can be substantial. Organizations need to plan for long-term data retention and storage capacity.
Continuous Monitoring and Updates
Cyber threats evolve rapidly. Security systems must be continuously updated to detect new threats. This requires staying current with the latest threat intelligence and adjusting the system accordingly.
Cloud Environments
Managing security in cloud environments adds complexity, as traditional SIEM solutions may not fully support or integrate with cloud-based systems without additional configurations and tools.
Complexity of Reporting
Extracting meaningful information and reports from the security solution can be complex. This is especially challenging when presenting information to non-technical stakeholders.
How Network Detection and Response Makes SIEM Smarter
Network Detection and Response (NDR) and Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) solutions are both critical components of a modern cybersecurity strategy, but they serve different purposes.
NDR focuses on monitoring and detecting threats within the network, while SIEM solutions focus on collecting and analyzing data from various sources to provide a comprehensive view of an organization’s security posture.
When used together, NDR can enhance the capabilities of these systems in several ways, making it smarter and more effective.
NDR and EDR/XDR: Evolution of cyber defense stacks
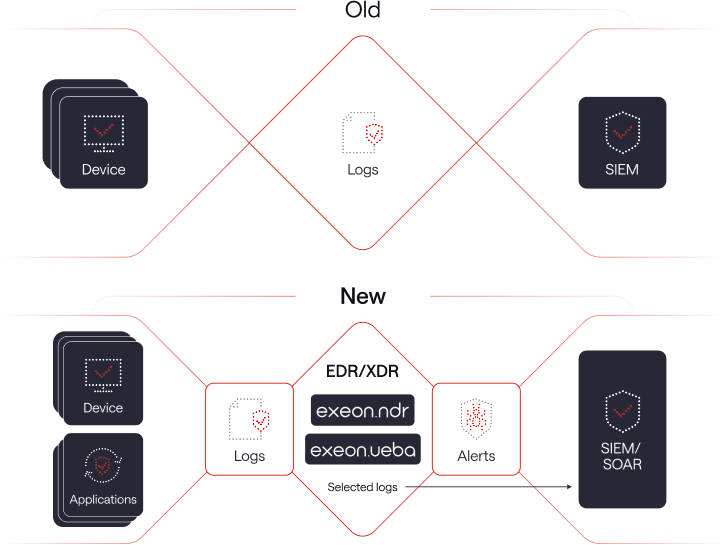
Real-time Threat Detection
NDR solutions are designed to provide real-time threat detection by continuously monitoring network traffic and looking for anomalies or suspicious activities.
This immediate detection can complement traditional security systems, which often rely on log data that may not be immediately available.
By integrating NDR, you can feed real-time threat data directly into your security system, enabling faster response to threats.
Enhanced Contextual Data
NDR solutions can provide rich contextual data about network traffic and user behavior, such as packet-level data, flow data, and user behavior analytics.
This additional context can help better understand the nature and scope of security incidents, allowing for more accurate threat identification and response.
Reduced False Positives
NDR tools are designed to reduce false positives by applying sophisticated analytics to network traffic data.
By reducing the noise in the data, security systems can focus on more relevant and high-impact security events, making the overall security monitoring process more efficient and effective.
Improved Incident Response
NDR solutions can help SIEMs automate incident response by providing real-time information about emerging threats.
When NDR detects a suspicious event, it can trigger automated responses within the SIEM solution, such as alerting security teams or initiating predefined security workflows.
Correlation of Network and Endpoint Data
NDR solutions often integrate with endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools, allowing for the correlation of network and endpoint data.
This integration enables SIEM to provide a more comprehensive view of an attack’s progression across the network and endpoints, improving threat detection and response.
Threat Hunting
NDR can assist in threat hunting by providing security analysts with the ability to proactively search for signs of hidden threats within the network.
The results of threat hunting efforts can be incorporated into SIEM solutions for long-term analysis and trend identification.
Compliance and Reporting
SIEM is often used for compliance and reporting purposes. NDR can help ensure that network traffic data is accurately and comprehensively captured for compliance requirements.
This helps organizations meet regulatory standards and provides a more complete audit trail.
In summary, NDR makes SIEM solutions smarter by enhancing its capabilities with real-time threat detection, contextual data, reduced false positives, improved incident response, and better integration with network and endpoint security tools.
When used together, NDR and SIEM create a more robust and proactive security posture, helping organizations detect and respond to threats more effectively.
Quick, ready-to-go algorithms that detect complex threats
The machine learning Network Detection and Response (NDR) platform Exeon.NDR offers the flexibility to complement or replace a traditional system.
Regardless of your choice, Exeon.NDR delivers top-tier security analytics and renowned AI algorithms, along with pre-built threat analyzers crafted in Switzerland by a skilled team comprising data scientists, machine learning experts, ethical hackers, and network security specialists.
Exeon.NDR transforms your security solution, such as SIEM, Elasticsearch or ArcSight into an effective network alarm system.
Say goodbye to manual analysis and rule development as you embrace preconfigured detection algorithms for immediate use.
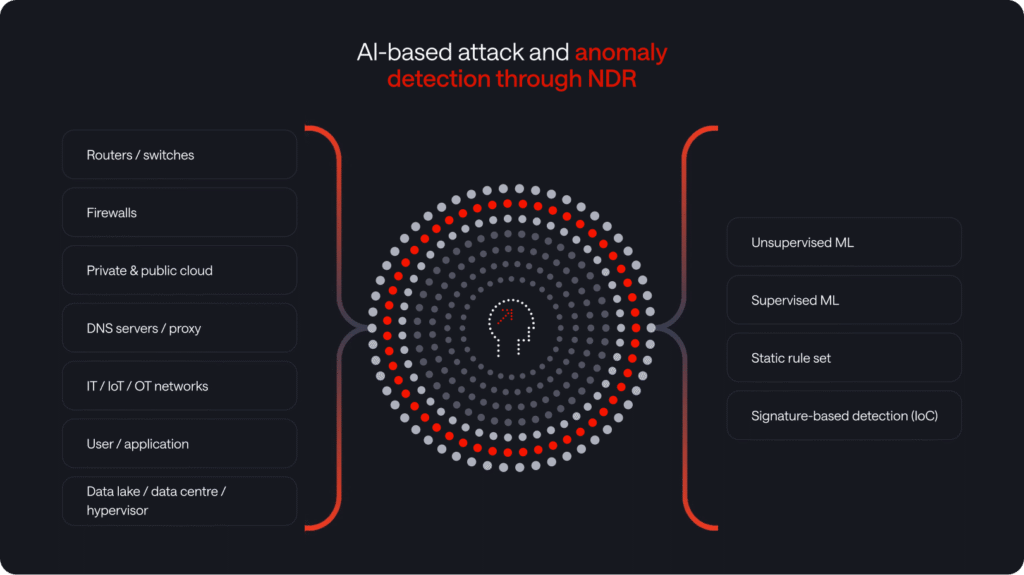
In a nutshell: ways NDR fills SIEM gaps
NDR solutions enhance an organization’s security posture by providing real-time, behavior-based threat detection, visibility into encrypted traffic, rapid incident response, and automated threat triage.
By complementing SIEM systems, NDR helps organizations bridge the gaps in their cybersecurity strategy, creating a more comprehensive defense against a wide range of threats.
- Real-Time Visibility: They provide real-time visibility into network traffic, which helps in identifying and responding to threats as they happen. This complements SIEM, which often relies on log data and may have a delay in detection.
- Behavior-Based Detection: It focuses on analyzing network traffic and endpoints for unusual or suspicious behaviors, which can identify threats that may not generate explicit log entries. SIEM, on the other hand, is more rule-based.
- Threat Detection at Scale: NDR can effectively analyze network traffic across the entire organization, making it well-suited for large-scale environments. SIEM may struggle to provide detailed analysis at such scale.
- Automatic Threat Triage: These solutions use machine learning and behavioral analytics to automatically prioritize and triage security alerts, reducing the workload for security teams. SIEM typically generates a high volume of alerts that require manual analysis.
- Visibility into Encrypted Traffic: NDR can inspect encrypted traffic, providing insights into encrypted threats that SIEM may struggle to analyze without decryption capabilities.
- Rapid Incident Response: NDR solutions enable rapid incident response by providing contextual information about the source and target of threats, which can help security teams take swift action. SIEM may require more time to piece together this information.
- Forensics and Investigation: These solutions retain historical network traffic data, allowing for in-depth forensics and investigations. SIEM may store logs, but often lacks the same level of network traffic detail.
- Reducing False Positives: They focus on reducing false positives by correlating network behavior, providing context, and using machine learning to identify genuine threats. SIEM, due to its reliance on logs, may generate more false positives.
- Integration with SIEM: NDR solutions can integrate traditional security, enhancing the capabilities of both systems. NDR can provide enriched data to SIEM for more comprehensive analysis.
- Cloud and Hybrid Environments: NDR solutions extend their visibility and threat detection capabilities into cloud and hybrid environments.
- Anomaly Detection: They excel at identifying deviations from normal network behavior, making them effective in detecting insider threats and zero-day attacks, where predefined SIEM rules may not apply.
Established use cases and extensive experience in security analytics
By utilizing your current data resources, you have the flexibility to determine what information should be supplied via your SIEM and what should be drawn directly from your IT network sources, such as Firewalls and Secure Web Gateways.
Employing specialized algorithms, Exeon.NDR promptly employs established use cases and the extensive experience of years in security analytics to swiftly identify cyber intruders and malicious insiders, eliminating the need for laborious manual analysis, intricate rule configurations, costly customizations, or the addition of extra hardware sensors.
Simply deploying Exeon.NDR can transform your SIEM into an efficient AI-driven network security system
Additionally, any identified threats and alerts can seamlessly integrate into your SIEM through a REST API, supporting your existing workflows.
Unique visualizations are also available to enhance your comprehension of your network’s data patterns.
Deploying Exeon.NDR is a quick process, as it directly utilizes your current IT infrastructure as sensors.
Book your free tour and consultation with us today to see it live!