Definition
An Intrusion Detection System (IDS) is a crucial component of network security that involves monitoring and analyzing network traffic to identify unauthorized access attempts, security breaches, and potentially harmful activities.
A network intrusion detection system (NIDS) is a specific type of IDS that focuses on monitoring and analyzing network traffic to identify potential threats. This proactive approach empowers businesses to detect and respond swiftly to cyber threats, minimizing potential damage and data loss.
IDS is a critical component of modern cybersecurity. It is designed to monitor and analyze network traffic for signs of unauthorized access, security breaches, and potential threats.
Its primary objective is to proactively detect and respond to cyber incidents, ensuring the protection of sensitive data and network infrastructure.
Types of Intrusion Detection Systems
Network-Based Intrusion Detection Systems (NIDS)
Network-Based Intrusion Detection Systems monitor network traffic in real-time, examining data packets for suspicious patterns and known attack signatures.
Network intrusion detection systems can be placed strategically throughout the network to ensure comprehensive coverage.
Host-Based Intrusion Detection Systems (HIDS)
Host-Based Intrusion Detection Systems focus on individual devices, monitoring activities on specific hosts or servers.
HIDS provides an additional layer of protection by identifying potential threats that may not be visible at the network level.
How it works: 2 main principles
- Signature-Based Detection: Signature-Based Detection relies on a vast database of known attack signatures. As network traffic passes through the intrusion detection system, it compares incoming data packets against this database, triggering alerts when matches are found.
- Anomaly-Based Detection: Anomaly-Based Detection establishes a baseline of normal network behavior. When the IDS detects any deviations from this baseline, it raises alerts, indicating potential intrusion attempts or suspicious activities.
Intrusion Detection System vs.
Intrusion Prevention System
An Intrusion Detection System (IDS) and an Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) are both essential components of network security, but they serve different purposes.
An IDS is a passive system that monitors network traffic and alerts security teams to potential threats. It analyzes incoming network traffic for signs of malicious activity and generates alerts when suspicious patterns are detected. This allows security teams to investigate and respond to potential threats.
In contrast, an IPS is an active system that not only detects but also prevents malicious activity. When an IPS identifies malicious packets, it can block them in real-time, preventing them from reaching their intended destination. This proactive approach helps to stop attacks before they can cause harm.
While an IDS provides valuable insights and alerts, an IPS takes immediate action to protect the network.
By combining both IDS and IPS, organizations can achieve a comprehensive network security strategy that detects and prevents threats, ensuring robust protection against cyberattacks.
IDS Detection Methods
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) employ various detection methods to identify malicious activity within network traffic. The most common methods include:
- Signature-Based Detection: This method relies on a database of known attack signatures. As network packets flow through the intrusion detection system, they are compared against this database. If a match is found, an alert is triggered. This method is highly effective for detecting known threats but may struggle with new or unknown attack patterns.
- Anomaly-Based Detection: This method establishes a baseline of normal network behavior. Any deviation from this baseline is flagged as suspicious. Anomaly-based detection is useful for identifying new or unknown threats, as it focuses on unusual behavior rather than specific attack signatures. However, it may generate false positives if the baseline is not accurately defined.
- Hybrid Detection: Combining the strengths of both signature-based and anomaly-based detection, hybrid detection provides a more comprehensive approach. It uses known attack signatures to quickly identify familiar threats while also monitoring for anomalies that may indicate new or sophisticated attacks. This dual approach enhances the overall effectiveness of the IDS.
By utilizing these detection methods, intrusion detection systems can effectively monitor network traffic and identify potential threats, providing a critical layer of security for organizations.
Evasion Techniques
Cybercriminals employ various techniques to evade detection by Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS), making it challenging for security teams to identify and mitigate threats.
Some common evasion techniques include:
- Encryption: Attackers encrypt malicious traffic to prevent IDS from analyzing its content. Encrypted traffic can bypass traditional detection methods, making it difficult to identify threats hidden within.
- Obfuscation: Malicious traffic is disguised as legitimate traffic to avoid detection. This can involve altering the appearance of the traffic or using techniques to blend in with normal network activity.
- Tunneling: Malicious traffic is hidden within legitimate traffic, such as encapsulating harmful data within standard protocols. This makes it harder for intrusion detection systems to distinguish between benign and malicious packets.
- Proxy Servers and VPNs: Attackers use proxy servers, VPNs, and botnets to mask their true origin and evade detection. Incorrectly configured proxy servers can also be exploited to bypass IDS.
These evasion techniques highlight the need for advanced detection methods and continuous monitoring to stay ahead of sophisticated attackers.
Insider Threat Detection
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) are not only effective against external threats but also play a crucial role in detecting insider threats. Insider threats involve malicious activities carried out by authorized personnel within an organization, making them particularly challenging to identify.
Intrusion detection systems can monitor network traffic and system calls to detect unusual behavior that may indicate an insider threat. For example, if an employee accesses sensitive data outside of their normal working hours or transfers large amounts of data to an external location, the IDS can flag this activity as suspicious.
By continuously analyzing network traffic and user behavior, IDS can help security teams identify potential insider threats early, allowing for timely intervention and mitigation. This capability is essential for protecting sensitive data and maintaining the integrity of the organization’s network.
Role of Machine Learning in IDS
Machine learning has revolutionized the capabilities of Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) by enabling them to analyze incoming network traffic and detect anomalies that may indicate malicious activity.
Traditional detection methods, such as signature-based detection, rely on predefined attack signatures, which can be limited in identifying new or unknown threats.
Machine learning algorithms, on the other hand, can be trained on large datasets of network traffic to identify patterns and anomalies. These algorithms continuously learn and adapt, improving their ability to detect zero-day attacks and other sophisticated threats that may not be detectable by traditional methods.
By leveraging machine learning, intrusion detection systems can analyze vast amounts of incoming network traffic in real-time, identifying subtle deviations from normal behavior that may indicate a potential threat.
This advanced detection method enhances the overall effectiveness of IDS, providing organizations with a powerful tool to protect against evolving cyber threats.
Benefits
Implementing an effective Intrusion Detection System offers several key advantages:
- Early Threat Detection: by continuously monitoring network activities, Intrusion Detection enables early detection of potential threats, preventing cyber incidents before they escalate.
- Incident Response Improvement: it provides security teams with real-time alerts and valuable insights, facilitating swift and effective incident response to mitigate potential damages.
- Protecting Sensitive Data: With the ability to identify unauthorized access attempts, Intrusion Detection plays a vital role in safeguarding sensitive data from falling into the wrong hands.
Best practices
To optimize its effectiveness, consider the following best practices:
- Regular Updates and Maintenance: Keep the intrusion detection system up-to-date with the latest threat signatures and software patches to stay ahead of emerging cyber threats.
- Integration with Security Infrastructure: integrate it with existing security infrastructure, such as firewalls and SIEM, to create a comprehensive and cohesive security ecosystem.
- Ongoing Monitoring and Analysis: Consistently monitor and analyze network traffic to identify new threats and enhance the accuracy of anomaly detection.

Limitations
In contrast to the many benefits of implementing an IDS system, there are also some limitations:
- False Positives and False Negatives: Intrusion detection systems may produce false positives, indicating potential threats that are not actual breaches, and false negatives, missing genuine security threats due to evasion techniques or new attack patterns.
- Dependence on Signature Updates: Signature-Based IDS requires regular updates to its signature database to detect new attack patterns, outdated databases may lead to missing emerging threats.
- Limited Visibility in Encrypted Traffic: It struggles to analyze encrypted traffic, limiting its effectiveness in detecting threats hidden within encrypted communications.
- Resource Intensive: It can be resource-intensive for high-traffic networks, causing performance issues due to continuous monitoring and analysis.
- Inability to Prevent Attacks: It serves as a detection tool and cannot actively prevent attacks, necessitating complementary Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) for real-time mitigation.
- Lack of Contextual Understanding: It may lack contextual insight into network activities, making it challenging to assess the severity of detected incidents accurately.
- Evasion Techniques: Sophisticated attackers may evade IDS detection using various techniques, reducing its effectiveness in identifying such threats.

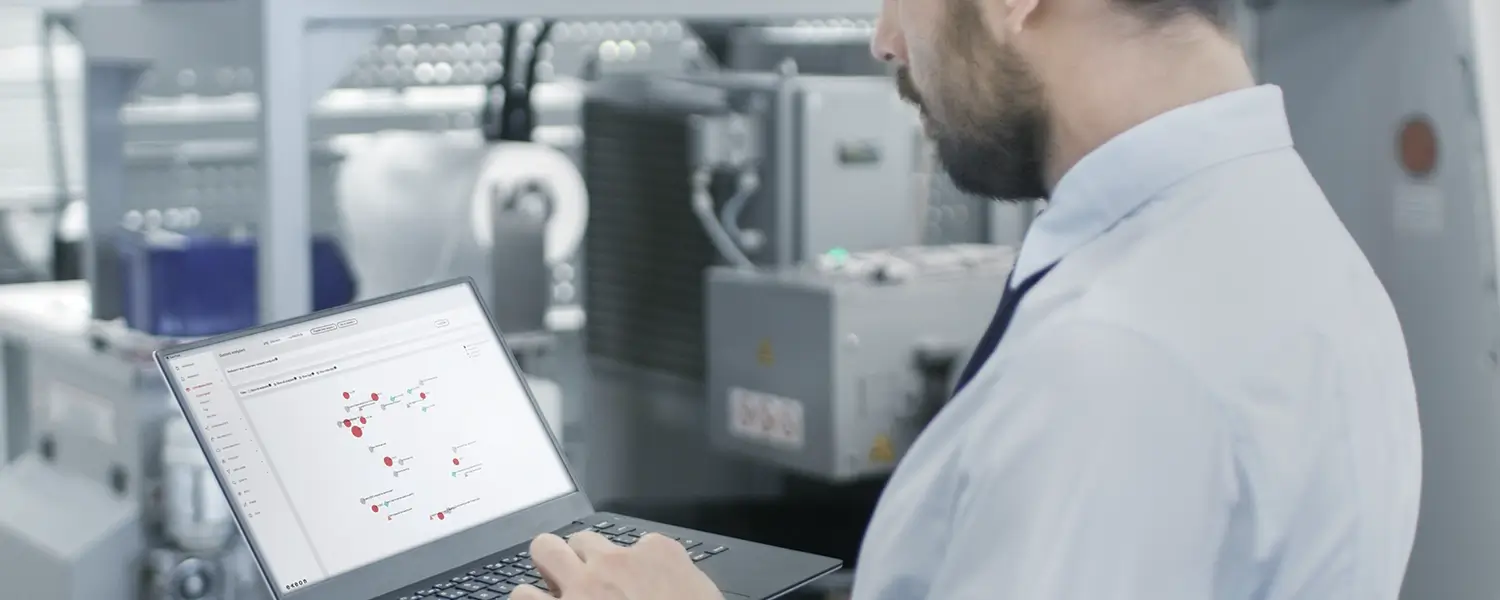
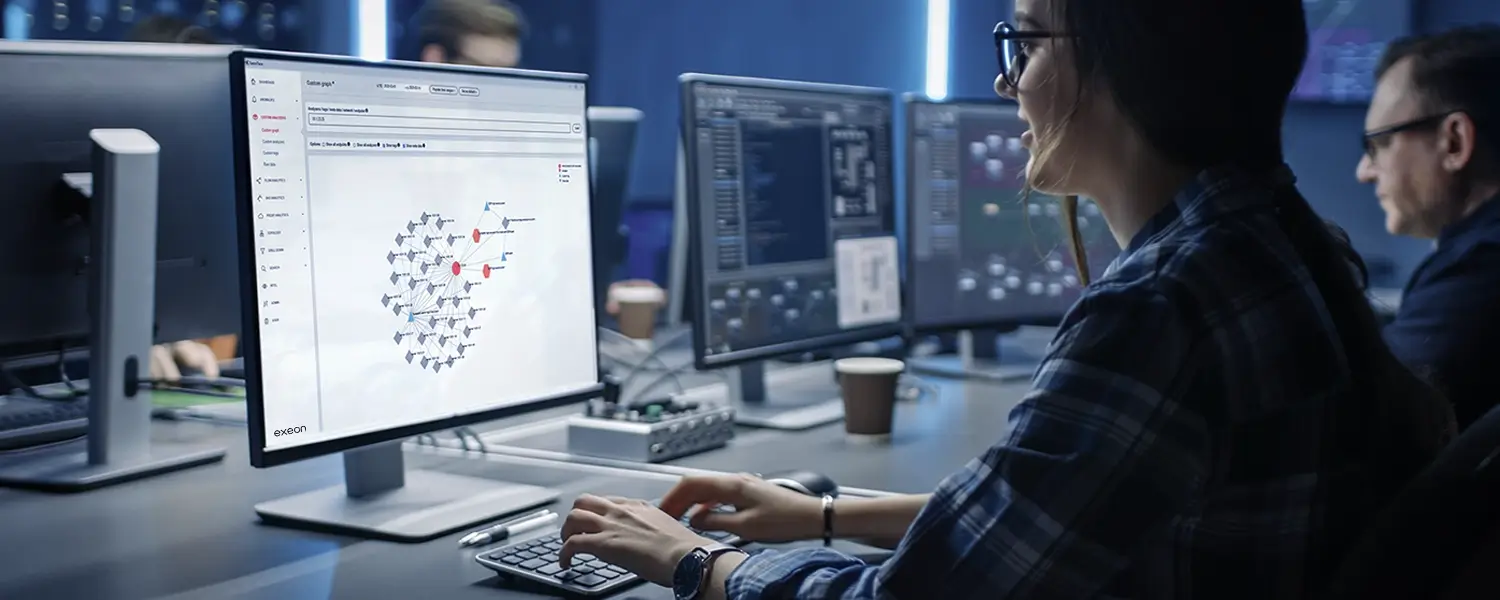
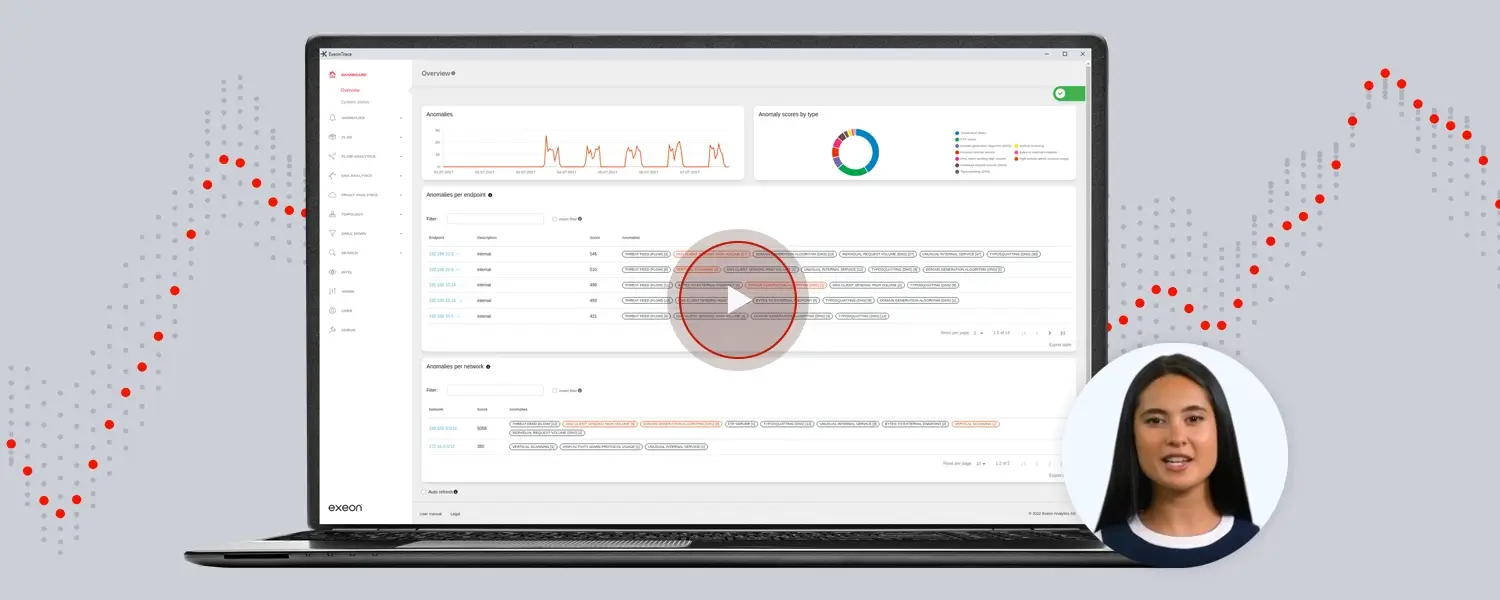
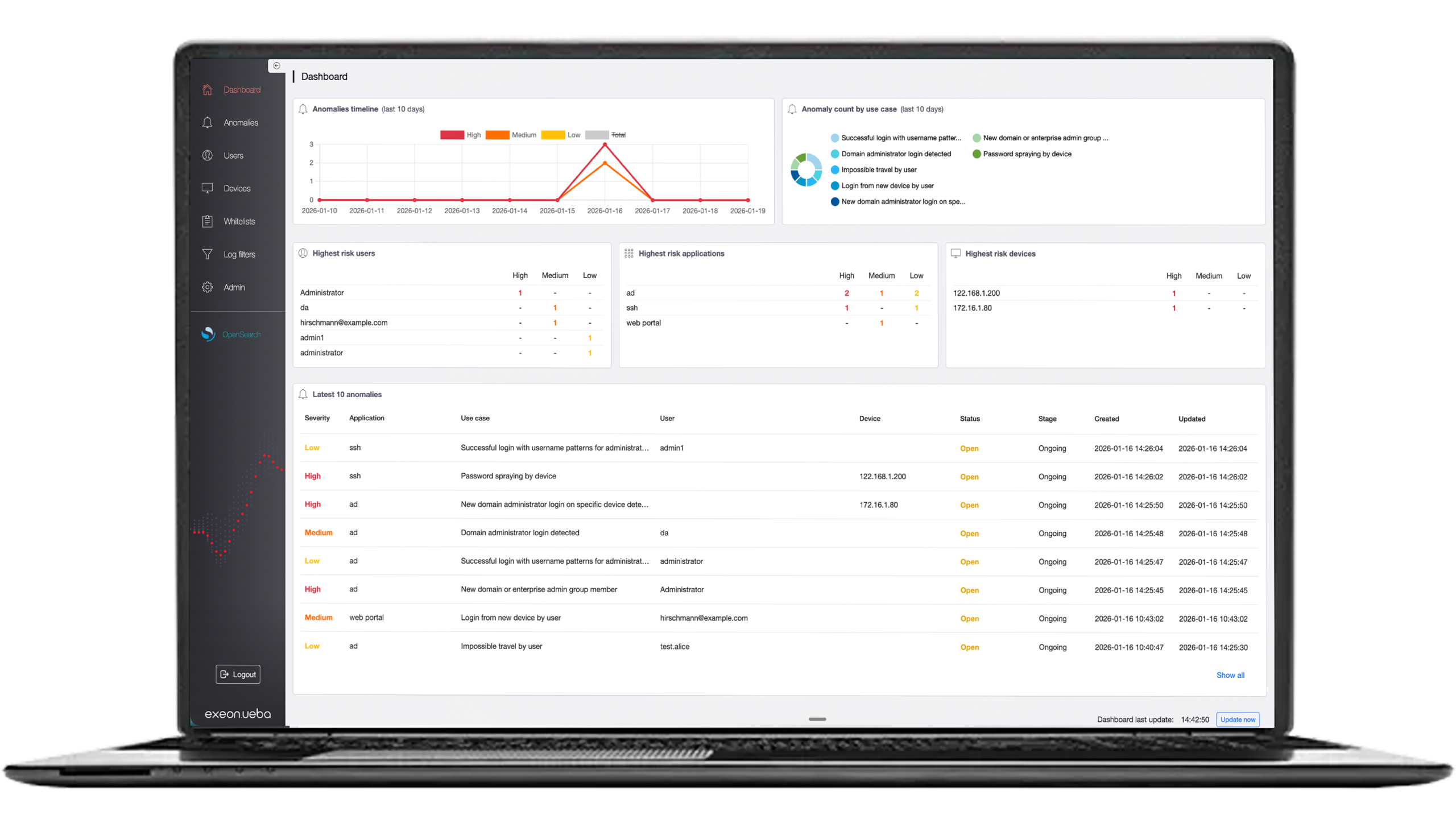
Exeon.NDR, used by a security team in this image, closes the gaps of IDS and acts as a future-proof shield in the evolving cybersecurity landscape thanks to its powerful AI and ML methodology.
How NDR addresses IDS limitations
Exeon.NDR, as an advanced Network Detection and Response (NDR) solution, offers several features that help overcome the limitations of traditional Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and provide enhanced network security.
Signature-Free Detection:
Exeon.NDR does not rely on pre-programmed signatures for threat detection. Instead, it utilizes sophisticated analytical protocols and machine learning algorithms to inspect network communications in near real-time.
This approach enables the NDR system to detect anomalous network behavior and unknown threats that intrusion detection systems might miss due to outdated or limited signature databases.
Detection of Zero-Day Attacks:
With Exeon’s ability to detect unknown threats, including zero-day attacks that have no existing signatures, organizations can stay ahead of emerging cyber threats.
This proactive detection capability is essential in defending against the latest attack vectors, providing an edge in the ever-changing threat landscape.
Inspection of Encrypted Traffic:
Exeon’s metadata analysis-based approach allows it to inspect all network communications, even if they are encrypted. Unlike traditional NDR providers relying on deep packet inspection and IPS/IDS, Exeon.NDR is not blind to a significant percentage of network traffic hidden within encrypted payloads.
This capability is crucial as many threat actors employ encryption in their attack protocols to evade intrusion detection.
Network Forensics and Incident Investigations:
One of the key strengths of Exeon lies in its ability to retain an archive of past network activities. This enables comprehensive network forensics and facilitates incident investigations. Security teams can examine historical network data to identify the source and impact of security incidents.
This information aids in preventing the recurrence of similar security breaches and enhances incident response effectiveness.